
Advanced multilayer security
Elevate the security posture of your organization starting with the operating system.
Hybrid capabilities with Azure
Extend your datacenter to Azure for greater IT efficiency.
Flexible application platform
Empower developers and IT pros with an application platform to build and deploy diverse applications.

Unbeatable offers on Azure
See how your cost savings will add up on Azure with offers such as Azure Hybrid Benefit and Extended Security Updates.
What’s new in Windows Server 2022
Security
The new security capabilities in Windows Server 2022 combine other security capabilities in Windows Server across multiple areas to provide defense-in-depth protection against advanced threats. Advanced multi-layer security in Windows Server 2022 provides the comprehensive protection that servers need today.
Secured-core server
Certified Secured-core server hardware from an OEM partner provides additional security protections that are useful against sophisticated attacks. This can provide increased assurance when handling mission critical data in some of the most data sensitive industries. A Secured-core server uses hardware, firmware, and driver capabilities to enable advanced Windows Server security features. Many of these features are available in Windows Secured-core PCs and are now also available with Secured-core server hardware and Windows Server 2022.
Hardware root-of-trust
Trusted Platform Module 2.0 (TPM 2.0) secure crypto-processor chips provide a secure, hardware-based store for sensitive cryptographic keys and data, including systems integrity measurements. TPM 2.0 can verify that the server has been started with legitimate code and can be trusted by subsequent code execution. This is known as a hardware root-of-trust and is used by features such as BitLocker drive encryption.
Virtualization-based security (VBS)
Secured-core servers support virtualization-based security (VBS) and hypervisor-based code integrity (HVCI). VBS uses hardware virtualization features to create and isolate a secure region of memory from the normal operating system, protecting against an entire class of vulnerabilities used in cryptocurrency mining attacks. VBS also allows for the use of Credential Guard, where user credentials and secrets are stored in a virtual container that the operating system cannot access directly.
Firmware protection
Firmware executes with high privileges and is often invisible to traditional anti-virus solutions, which has lead to a rise in the number of firmware-based attacks. Secured-core server processors support measurement and verification of boot processes with Dynamic Root of Trust for Measurement (DRTM) technology and isolation of driver access to memory with Direct Memory Access (DMA) protection.
HVCI uses VBS to significantly strengthen code integrity policy enforcement, including kernel mode integrity which checks all kernel mode drivers and binaries in a virtualized environment before they are started, preventing unsigned drivers or system files from being loaded into system memory.
Secure connectivity
Transport: HTTPS and TLS 1.3 enabled by default on Windows Server 2022
Secure connections are at the heart of today’s interconnected systems. Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.3 is the latest version of the internet’s most deployed security protocol, which encrypts data to provide a secure communication channel between two endpoints. HTTPS and TLS 1.3 is now enabled by default on Windows Server 2022, protecting the data of clients connecting to the server. It eliminates obsolete cryptographic algorithms, enhances security over older versions, and aims to encrypt as much of the handshake as possible. Learn more about supported TLS versions and about supported cipher suites.
Server Message Block (SMB): SMB AES-256 encryption for the most security conscious
Windows Server now supports AES-256-GCM and AES-256-CCM cryptographic suites for SMB encryption and signing. Windows will automatically negotiate this more advanced cipher method when connecting to another computer that also supports it, and it can also be mandated through Group Policy. Windows Server still supports AES-128 for down-level compatibility.
Secure DNS: Encrypted DNS name resolution requests with DNS-over-HTTPS
DNS Client in Windows Server 2022 now supports DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) which encrypts DNS queries using the HTTPS protocol. This helps keep your traffic as private as possible by preventing eavesdropping and your DNS data being manipulated. Learn more about configuring the DNS client to use DoH.
SMB: East-West SMB encryption controls for internal cluster communications
Windows Server failover clusters now support granular control of encrypting and signing intra-node storage communications for Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) and the storage bus layer (SBL). This means that when using Storage Spaces Direct, you can decide to encrypt or sign east-west communications within the cluster itself for higher security.
SMB Direct and RDMA encryption
SMB Direct and RDMA supply high bandwidth, low latency networking fabric for workloads like Storage Spaces Direct, Storage Replica, Hyper-V, Scale-out File Server, and SQL Server. SMB Direct in Windows Server 2022 now supports encryption. Previously, enabling SMB encryption disabled direct data placement; this was intentional, but seriously impacted performance. Now data is encrypted data before placement, leading to far less performance degradation while adding AES-128 and AES-256 protected packet privacy.
SMB over QUIC
SMB over QUIC updates the SMB 3.1.1 protocol in Windows Server 2022 Datacenter: Azure Edition and supported Windows clients to use the QUIC protocol instead of TCP. By using SMB over QUIC along with TLS 1.3, users and applications can securely and reliably access data from edge file servers running in Azure. Mobile and telecommuter users no longer need a VPN to access their file servers over SMB when on Windows. More information can be found at the SMB over QUIC documentation.
Azure hybrid capabilities
You can increase your efficiency and agility with built-in hybrid capabilities in Windows Server 2022 that allow you to extend your data centers to Azure more easily than ever before.
Azure Arc enabled Windows Servers
Azure Arc enabled servers with Windows Server 2022 brings on-premises and multi-cloud Windows Servers to Azure with Azure Arc. This management experience is designed to be consistent with how you manage native Azure virtual machines. When a hybrid machine is connected to Azure, it becomes a connected machine and is treated as a resource in Azure. More information can be found at the Azure Arc enables servers documentation.
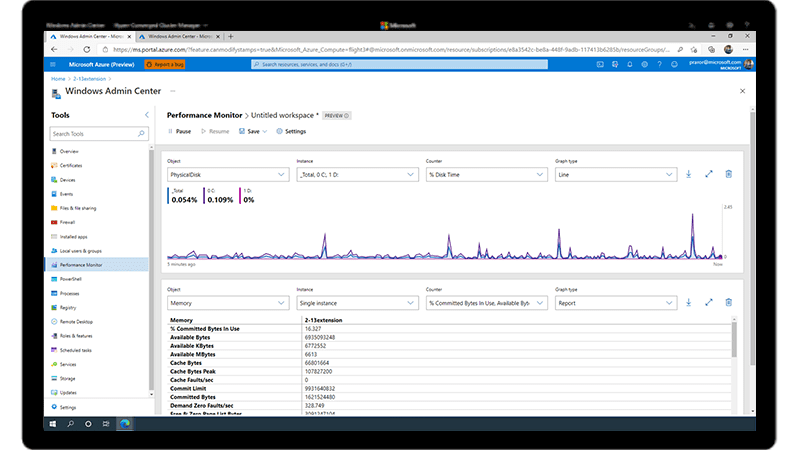
Windows Admin Center
Improvements to Windows Admin Center to manage Windows Server 2022 include capabilities to both report on the current state of the Secured-core features mentioned above, and where applicable, allow customers to enable the features. More information on these and many more improvements to Windows Admin Center can be found at the Windows Admin Center documentation.
Application platform
There are several platform improvements for Windows Containers, including application compatibility and the Windows Container experience with Kubernetes. A major improvement includes reducing the Windows Container image size by up to 40%, which leads to a 30% faster startup time and better performance.
You can now also run applications that depend on Azure Active Directory with group Managed Services Accounts (gMSA) without domain joining the container host, and Windows Containers now support Microsoft Distributed Transaction Control (MSDTC) and Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ).
There are several other enhancements that simplify the Windows Container experience with Kubernetes. These enhancements include support for host-process containers for node configuration, IPv6, and consistent network policy implementation with Calico.
In addition to platform improvements, Windows Admin Center has been updated to make it easy to containerize .NET applications. Once the application is in a container, you can host it on Azure Container Registry to then deploy it to other Azure services, including Azure Kubernetes Service.
With support for Intel Ice Lake processors, Windows Server 2022 supports business-critical and large-scale applications, such as SQL Server, that require up to 48 TB of memory and 2,048 logical cores running on 64 physical sockets. Confidential computing with Intel Secured Guard Extension (SGX) on Intel Ice Lake improves application security by isolating applications from each other with protected memory.
Azure Automanage – Hotpatch
Hotpatch, part of Azure Automanage, is supported in Windows Server 2022 Datacenter: Azure Edition. Hotpatching is a new way to install updates on new Windows Server Azure Edition virtual machines (VMs) that doesn’t require a reboot after installation. More information can be found at the Azure Automanage documentation.
Other key features
Nested virtualization for AMD processors
Nested virtualization is a feature that allows you to run Hyper-V inside of a Hyper-V virtual machine (VM). Windows Server 2022 brings support for nested virtualization using AMD processors, giving more choices of hardware for your environments. More information can be found at the nested virtualization documentation.
Microsoft Edge browser
Microsoft Edge is included with Windows Server 2022, replacing Internet Explorer. It is built on Chromium open source and backed by Microsoft security and innovation. It can be used with Server Core or Server with Desktop Experience installation options. More information can be found at the Microsoft Edge Enterprise documentation. Note that Microsoft Edge, unlike the rest of Windows Server, follows the Modern Lifecycle for its support lifecycle. For details, see Microsoft Edge lifecycle documentation.
Networking performance
UDP performance improvements
UDP is becoming a very popular protocol carrying more and more network traffic. The increasing popularity of RTP and custom (UDP) streaming and gaming protocols The QUIC protocol, built on top of UDP, brings the performance of UDP to a level on par with TCP. Significantly, Windows Server 2022 includes UDP Segmentation Offload (USO). USO moves most of the work required to send UDP packets from the CPU to the network adapter’s specialized hardware. Complimenting USO is UDP Receive Side Coalescing (UDP RSC), which coalesces packets and reduces CPU usage for UDP processing. In addition, we have also made hundreds of improvements to the UDP data path both transmit and receive. Windows Server 2022 and Windows 11 both have this new capability.
Hyper-V virtual switch improvements
Virtual switches in Hyper-V have been enhanced with updated Receive Segment Coalescing (RSC). This allows the hypervisor network to coalesce packets and process as one larger segment. CPU cycles are reduced and segments will remain coalesced across the entire data path until processed by the intended application. This means improved performance in both network traffic from an external host, received by a virtual NIC, as well as from a virtual NIC to another virtual NIC on the same host.
TCP performance improvements
Windows Server 2022 uses TCP HyStart++ to reduce packet loss during connection start-up (especially in high-speed networks) and RACK to reduce Retransmit TimeOuts (RTO). These features are enabled in the transport stack by default and provide a smoother network data flow with better performance at high speeds. Windows Server 2022 and Windows 11 both have this new capability.
Storage
Storage Migration Service
Enhancements to Storage Migration Service in Windows Server 2022 makes it easier to migrate storage to Windows Server or to Azure from more source locations. Here are the features that are available when running the Storage Migration Server orchestrator on Windows Server 2022:
Storage bus cache with Storage Spaces on standalone servers
Storage bus cache is now available for standalone servers. It can significantly improve read and write performance, while maintaining storage efficiency and keeping the operational costs low. Similar to its implementation for Storage Spaces Direct, this feature binds together faster media (for example, NVMe or SSD) with slower media (for example, HDD) to create tiers. A portion of the faster media tier is reserved for the cache. To learn more, see Enable storage bus cache with Storage Spaces on standalone servers.
Migrate local users and groups to the new server.
- Migrate storage from failover clusters, migrate to failover clusters, and migrate between standalone servers and failover clusters.
- Migrate storage from a Linux server that uses Samba.
- More easily synchronize migrated shares into Azure by using Azure File Sync.
- Migrate to new networks such as Azure.
- Migrate NetApp CIFS servers from NetApp FAS arrays to Windows servers and clusters.
- Adjustable storage repair speed
User adjustable storage repair speed is a new feature in Storage Spaces Direct that offers more control over the data resync process by allocating resources to either repair data copies (resiliency) or run active workloads (performance). This helps improve availability and allows you to service your clusters more flexibly and efficiently.
SMB compression
Enhancement to SMB in Windows Server 2022 and Windows 11 allows a user or application to compress files as they transfer over the network. Users no longer have to manually zip files in order to transfer much faster on slower or more congested networks. For details, see SMB Compression.
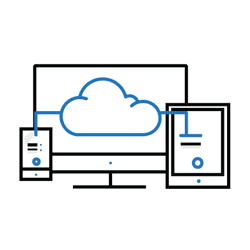
Hardware requirements for Windows Server
The minimum hardware requirements to run Windows Server. If your computer has less than the minimum requirements, you will not be able to install this product correctly. Actual requirements will vary based on your system configuration and the applications and features you install, Unless otherwise specified, these minimum hardware requirements apply to all installation options (Server Core and Server with Desktop Experience) and both Standard and Datacenter editions.
Important
The highly diverse scope of potential deployments makes it unrealistic to state recommended hardware requirements that would be generally applicable. Consult documentation for each of the server roles you intend to deploy for more details about the resource needs of particular server roles. For the best results, conduct test deployments to determine appropriate hardware requirements for your particular deployment scenarios.
Processor
Processor performance depends not only on the clock frequency of the processor, but also on the number of processor cores and the size of the processor cache. The following are the processor requirements for this product:
Minimum:
- 4 GHz 64-bit processor
- Compatible with x64 instruction set
- Supports NX and DEP
- Supports CMPXCHG16b, LAHF/SAHF, and PrefetchW
- Supports Second Level Address Translation (EPT or NPT)
Coreinfo, part of Windows Sysinternals, is a tool you can use to confirm which of these capabilities your CPU has.
RAM
The following are the estimated RAM requirements for this product:
Minimum:
- 512 MB (2 GB for Server with Desktop Experience installation option)
- ECC (Error Correcting Code) type or similar technology, for physical host deployments
Storage controller and disk space requirements
Computers that run Windows Server must include a storage adapter that is compliant with the PCI Express architecture specification. Persistent storage devices on servers classified as hard disk drives must not be PATA. Windows Server does not allow ATA/PATA/IDE/EIDE for boot, page, or data drives.
The following are the estimated minimum disk space requirements for the system partition.
Minimum: 32 GB
Network adapter requirements
Network adapters used with this release should include these features:
Minimum:
- An ethernet adapter capable of at least 1 gigabit per second throughput
- Compliant with the PCI Express architecture specification.
A network adapter that supports network debugging (KDNet) is useful, but not a minimum requirement.
A network adapter that supports the Pre-boot Execution Environment (PXE) is useful, but not a minimum requirement.
Note
A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) chip is required in order to use certain features such as BitLocker Drive Encryption. If your computer uses TPM, it must meet these requirements:
- Hardware-based TPMs must implement version 2.0 of the TPM specification.
- TPMs that implement version 2.0 must have an EK certificate that is either pre-provisioned to the TPM by the hardware vendor or be capable of being retrieved by the device during the first boot.
- TPMs that implement version 2.0 must ship with SHA-256 PCR banks and implement PCRs 0 through 23 for SHA-256. It is acceptable to ship TPMs with a single switchable PCR bank that can be used for both SHA-1 and SHA-256 measurements.
A UEFI option to turn off the TPM is not a requirement.
Other requirements
Computers running this release also must have the following:
- DVD drive (if you intend to install the operating system from DVD media)
The following items are only required for certain features:
- UEFI 2.3.1c-based system and firmware that supports secure boot
- Trusted Platform Module
- Graphics device and monitor capable of Super VGA (1024 x 768) or higher-resolution
- Keyboard and Microsoft mouse (or other compatible pointing device)
- Internet access (fees may apply)
Contact us to get more information
Why pay extra, when you can pay less?
